NVS, solving problems with artificial vision
SVS checks that the laser beam is centered, and uses the machine learning algorithms to monitor the state of the nozzle and reduce waste.
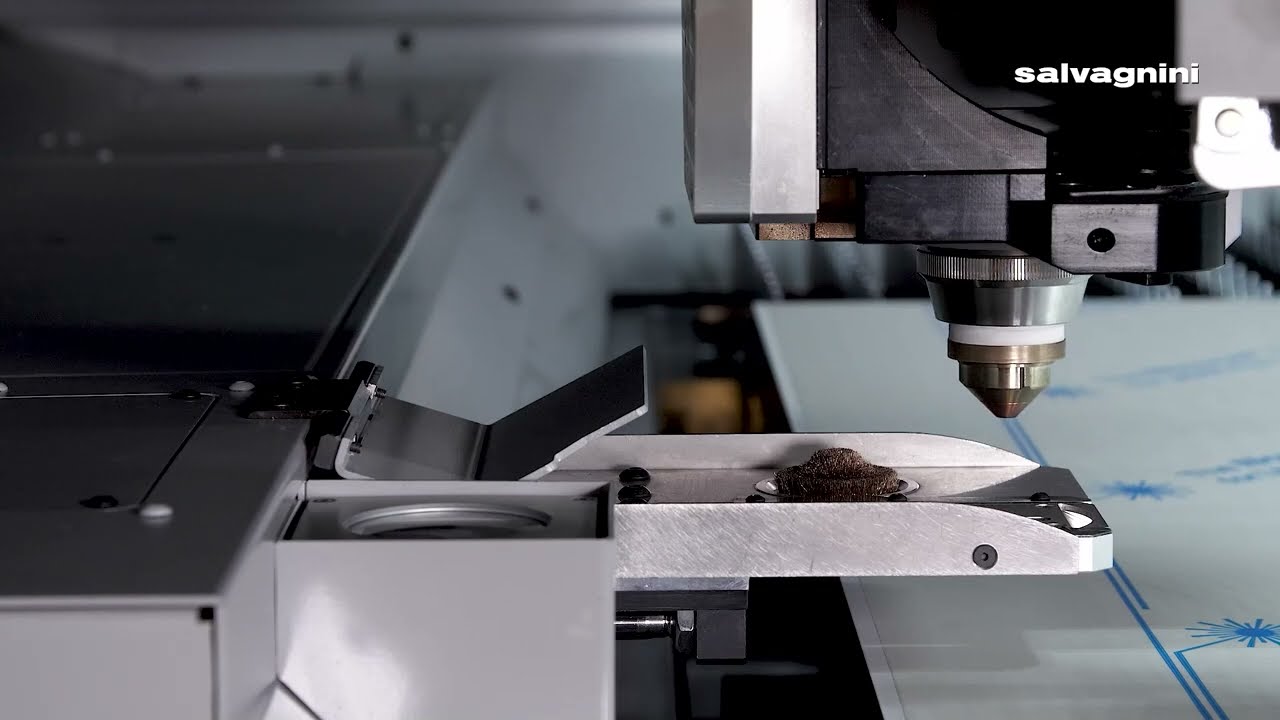
NVS was designed for two purposes: the first is to check the centering of the laser beam, the second is to check the state of the nozzle in terms of deformations or obstructions.
In the first case, NVS compares the actual diameter of the nozzle with what is stated in the program, and then proceeds to check that the beam is centered on the nozzle. The Salvagnini human-machine interface, FACE, has been enhanced with a laser centering tab – designed specifically for the NVS option: the system suggests any setting corrections needed, and these are then done manually by the operator.
To inspect the condition of the nozzle, on the other hand, NVS checks:
- any obstructions in the hole, which would reduce cutting quality;
- any deformations of the hole, which could cause problems for cutting quality, above all when cutting with oxygen;
- any deformations of the hole, which could cause problems for cutting quality, above all when cutting with oxygen.
Using the proprietary machine learning algorithms, the Salvagnini NVS classifies the condition of the nozzle with an intuitive “traffic light” system: in the FACE status bar, the nozzle is assessed as green, yellow or red. The traffic light system also suggests the required corrective actions: a green nozzle can still be used; a yellow nozzle must be checked and a red nozzle must be replaced. Combined with the ANC automatic nozzle changer option, the NVS is used to automatically replace a non-conforming nozzle with another of the same type.
NVS is an option available for the Salvagnini L3, L3.G4, and L5 laser models, whatever the size or power. By checking and rapidly and intuitively solving a number of imprecisions, it consistently reduces errors, waste and urgencies.